Executive Summary
Income Tax
- The procedure, Timeline, and Form has been specified for deposit the withholding tax deducted under section 194S relating to TDS on transfer of Virtual Digital Assets.
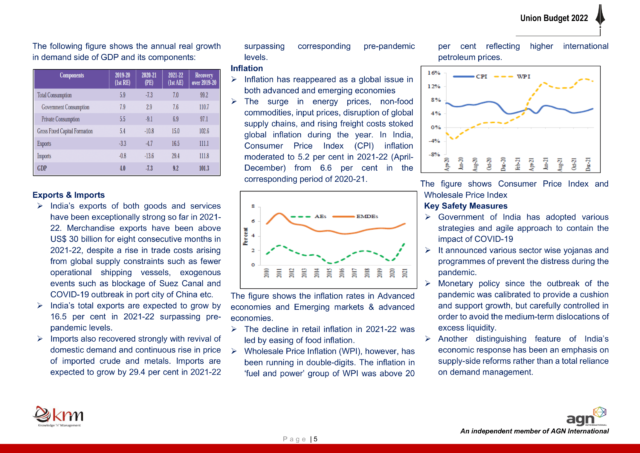
- Cost Inflation Index for Financial year 2022-23 is 331.
- Applicability of Safe Harbor Rules extended till Assessment year 2022-23.
Goods & Services Tax (GST) & Customs
- Guidelines issued for procedures relating to sanction, post-audit and review of refund claims.
- News and update has been issued to taxpayers for availing ITC as per law and GSTR-2B.
- New functionalities have been made available for taxpayers relating to Bank account validation, HSN validation and refund to un-registered persons.
Companies Act 2013/ Other Laws.
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has notified the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) Amendment Rules 2022
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has issued a notification to notify the Companies (Appointment and Qualification of Directors) Amendment Rules, 2022
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has issued a clarification w.r.t Micro-Finance/Micro Credit as an Object in the Object Clause of MOA of Section 8 companies registered under the Companies Act, 2013.
- SEBI has extended the timeline by one month to August 01, 2022, for commencing validation of all KYC records (new and existing) by (Know Your Client) Registration Agency (KRA).
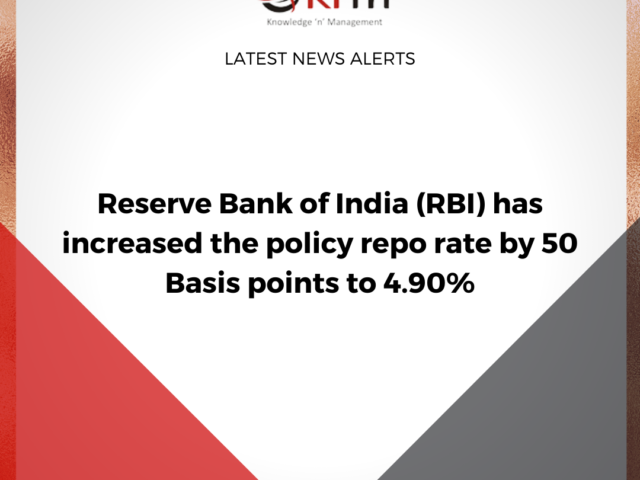
- RBI has decided to hike the Repo Rate by 50 basis points to 4.90% and the Standing Deposit Facility Rate stands adjusted to 4.65%, and the Marginal Standing Facility rate and Bank Rate to 5.15%.
Income Tax
- CBDT vide Notification No. 67/2022, dated 21 June 2022, issued the details relating to a time limit to deposit the withholding tax deducted u/s 194S relating to TDS on transfer of Virtual Digital Assets, form and manner of filing withholding tax return and the issue of tax deducted at source (TDS) certificate to deductee has now been prescribed by CBDT.
- TDS u/s 194S is required to be deposited to the Government of India within 30 days from the end of the month in which tax is deducted
- TDS return is to be submitted in the prescribed Challan-cum-statement in Form 26Q.
- TDS certificate in Form 16E to be issued to the deductee within 15 days from the due date of filing Form 26QE in a prescribed format.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 65/2022, dated 16 June 2022 has exempted/waived the requirement to withhold tax on payment of lease rent to a Unit located in IFSC for the lease of aircraft provided after complying with some prescribed conditions.
The exemption is applicable provided the lessor furnishes a declaration in Form no. 1 prescribed in the notification to the lessee giving details of 10 assessment years for which the lessor has opted for claiming deduction u/s 80LA(2) r.w.s 80LA(1A) of the Income-tax Act. The lessee shall not deduct tax at source for those 10 years on receipt of such declaration and make the disclosure accordingly in the withholding tax returns to be filed by the lessee (for other years, lessee shall continue to withhold tax at source).
- CBDT vide Notification No. 62/2022 dated 14 June 2022 notified the Cost Inflation Index for Financial year 2022-23 is 331. This notification shall come into force with effect from 1st April, 2023 and shall accordingly apply to the Assessment Year 2023-24 and subsequent years.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 57/2022 dated 31 May 2022 notified New Rule 44FA to provide form and manner of filing appeal to the High Court on ruling pronounced or order passed by the Board for Advance Rulings. The form and manner of filing appeal will be the same as the procedure laid down by the jurisdictional High Court for filing an appeal to the High Court.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 59/2022 dated 6 June 2022 provide relaxation of conditions for investment funds to whose fund manager is located in an International Financial Service Center Authority (IFSC).
- CBDT vide Notification No. 1 of 2022, dated 09 June 2022, enables the Compliance check functionality for Section 206AB & 206CCA of the Income-tax Act 1961 to facilitate tax Deductors and Collectors in identification of Specified persons.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 2 of 2022, dated 24 June 2022, Format, Procedure and Guidelines for submission of Form No. 1, Form No. 2 and Form No. 2A for Securities Transaction Tax (STT) has been issued. A new Form No. 2A has also been introduced as per the said notification, to be filed by Insurance Company for furnishing Securities Transaction Tax return along with procedures, formats and standards for ensuring secure capture and transmission of data.
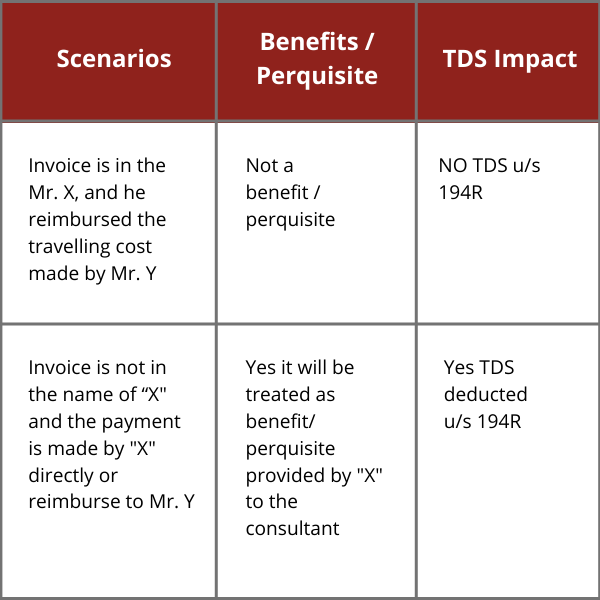
- Guidelines and clarification relating to Provisions of Section 194R issued dated 16.06.2022 on Tax on benefits or perquisites or Reformed Fringe Benefit Tax. For Detailed clarification, kindly refer link: https://knmindia.com/cases/section-194r-tax-on-benefit-or-perquisite-or-reformed-fringe-benefit-tax/.
International Taxation
- CBDT vide Notification No. 66 of 2022, dated 17 June 2022, Extends the Applicability of Safe Harbor Rules till Assessment year 2022-23. A list of eligible international transactions where the transfer price declared by the taxpayer shall be required to be accepted by the tax authorities (safe harbor) prescribed under Rule 10TD of the Income-tax Rules, 1962 extended until AY 2022-23.
Goods & Services Tax
- Guidelines No. 02/2022 dated 14 June 2022 issued for procedures relating to sanction, post-audit and review of refund claims which provides that
- the commissioner may review any decision or order, including an order of refund, with respect to its legality or propriety and he may direct any officer subordinate to him to file an appeal against the said decision or order within 6 months of the date of communication of the said decision or order.
- To ensure uniformity in processing of refund claims, while passing the refund sanction order in Form GST RFD-06, the proper officer should also upload a detailed speaking order along with refund sanction order in Form GST RFD-06.
- Details required in speaking order for all categories is clarified in order to ensure uniformity in issuance of such speaking order.
- ACES-GST portal provides the facility for uploading a document in pdf format along with the Form GST RFD-06 order. The same is made available to the refund applicant as well as Post-audit/ Reviewing Authority online.
- Updates has been issued for availing ITC as per law and GSTR-2B. For some of the taxpayers, there was an issue in relation to duplicate entries in GSTR2B which has since been fixed and correct GSTR 2B has been generated. In this regard, taxpayers while filing GSTR3B are advised to check and ensure that the value of ITC they are availing is correct as per the law.
They may check the correct ITC value from download of Auto drafted ITC statement GSTR2B or pdf of System Generated GSTR3B or on the ITC observed and prefilled GSTR-3B accordingly - New functionalities have been made available for taxpayers dated 06 June, 2022 as below:
- Bank Account validation status of taxpayers can be verified by registered taxpayers in their profile by clicking on the Bank Account Status link under Quick Links.
- Improvements made in filing process of GSTR-4 (Annual) for the taxpayers who opt for Composition Levy
- A phase wise AATO based validation has been built into the system to ensure that taxpayers with AATO of up-to Rs 5 crore have to report minimum 2 digit HSN and more than Rs 5 crore have to report minimum 4 digit HSN in table 12 of GSTR-1 in the phase 1 of HSN validation at the portal.
- The un-registered persons will now be able to apply for Temp User ID on GST Portal by selecting the reason for registration as, “To claim Refund”. They will be able to add their bank account details at the time of applying for Temp ID and subsequently edit their profile in respect of Authorized Signatory, Address and Bank Account details, if required. They can subsequently file for refund under the appropriate category on the Portal using their Temp ID credentials.
- Updates has been issued for availing ITC as per law and GSTR-2B. For some of the taxpayers, there was an issue in relation to duplicate entries in GSTR2B which has since been fixed and correct GSTR 2B has been generated. In this regard, taxpayers while filing GSTR3B are advised to check and ensure that the value of ITC they are availing is correct as per the law.
Companies Act, 2013
According to the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) amendment rules 2022, Rule 13 is amended to provide the revised penalty provision for non-compliance or contravention with any of the provisions. It is provided that any non-compliance or contravention with any of the provisions will attract a penalty of ₹5,000/- and where the contravention is a continuing one, a further fine of ₹500/- for every day during the period of contravention. This applies to offenses for which the penalty is not specified elsewhere in the law. The rule has been amended to drop a reference to Section 450 of the Companies Act which specifies a cap of ₹200,000/- in the case of a company and ₹50,000/- for an officer in default or any other person for offenses that persist.
MCA has tightened the norms for the appointment of any person, as director in an Indian Company, who is a national of a country that shares a land border with India. Accordingly, in case the person seeking appointment is a national of a country that shares a land border with India, necessary security clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs, the Government of India shall also be attached along with the consent. Further, no application number shall be generated in case of the person applying for the Director Identification Number is a national of a country that shares a land border with India, unless necessary security clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India has been attached along with an application for Director Identification Number.
The issues taken up in this report are based on a review of stakeholder suggestions, raised in stakeholder consultations conducted by the MCA and the IBBI or sent as public comments to the MCA. The Insolvency Law Committee in its 5th report has made key recommendations to strengthen the bankruptcy framework in India. Key recommendations include i) Mandating Reliance on IUs for Establishing Default; ii) Grant of exemptions from Scope of Moratorium only in exceptional circumstances; iii) Issues related to Avoidable Transactions and Improper Trading; iv) Curbing Submission of Unsolicited Resolution Plans and Revisions of Resolution Plans; v) Timeline for approval or rejection of resolution plan; vi) Standard of conduct of the Committee of Creditors (CoC); vii) Stakeholders Consultation Committee (SCC); viii) Secured Creditor’s Contribution; ix) Voluntary Liquidation Process: x) Operationalising the Insolvency & Bankruptcy Fund (IBC Fund); xi) Additional changes w.r.t Appellate mechanism for Orders issued under Section 220 etc. The recommendations of the committee will further strengthen the Insolvency & Bankruptcy framework in India by providing clarity and improving the process under the code. The committee will monitor further developments and keep striving to enhance the effectiveness of the Indian Insolvency framework.
The amendment is brought under Rule 6 which deals with compliances required by a person eligible and willing to restore his name in the independent director databank. Accordingly, any individual whose name has been removed from the databank may apply for restoration of his name on payment of fees of one thousand rupees and the institute shall allow such restoration subject to the conditions, that his name shall be shown in a separate restored category for a period of one year from the date of restoration within which, he shall be required to pass the online proficiency self-assessment test and thereafter his name shall be included in the databank, only, if he passes the said online proficiency self-assessment test and in such case, the fees paid by him at the time of initial registration shall continue to be valid for the period for which the same was initially paid; and in case he fails to pass the online proficiency self-assessment test within one year from the date of restoration, his name shall be removed from the data bank and he shall be required to apply afresh for inclusion of his name in the databank.
The amendment brought revisions to the procedure for striking off a company. Accordingly, where the Registrar, on examining the application made in Form STK-2, finds that it is necessary to call for further information or finds such application or any document annexed therewith is defective or incomplete in any respect, he shall inform the applicant to remove the defects and re-submit the complete Form within fifteen days from the date of such information, failing which the Registrar shall treat the Form as invalid in the electronic record, and shall inform the applicant. After the re-submission of the Form or document, if the Registrar finds that the Form or document is defective or incomplete in any respect, he shall give the further time of fifteen days to remove such defects or complete the Form, failing which the Registrar shall treat the Form as invalid in the electronic record and shall inform the applicant, accordingly. Any re-submission of the application in Form STK-2 made prior to the commencement of the Companies (Removal of Names of Companies from the Register of Companies) Amendment Rules, 2022 shall not be counted for the purposes of reckoning the maximum number of re-submissions of such Form.
Through this amendment, MCA has added a new sub-rule 4 in Rule 25A of the Companies (Compromises, Arrangements and Amalgamations) Rules, 2016, to provide that in case of a compromise or an arrangement or merger or demerger between an Indian company and a company or body corporate which has been incorporated in a country which shares a land border with India, a declaration in Form No. CAA-16 shall be required at the stage of submission of an application under Section 230 of the Act. Accordingly, a new Form CAA – 16 is also notified which is to be signed by the authorised representative of the companies involved and a declaration to be provided that whether the company/body corporate is not required to obtain prior approval under the Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019 or not. A copy of the approval is also required to be attached with the Form CAA-16.
MCA has been observed that various Section 8 companies are altering their object clause for carrying out micro-finance activities by way of passing Special Resolution, changing Activity code and subsequently filing of e-form MGT-14 with the concerned ROCs, even though at initial incorporation, the ROC (CRC) is not allowing Section 8 companies to get incorporated with the objects of microfinance activities in view of Ministry’s direction letter no. No. 05/33/2017-CL.V dated 10.02.2020 and letter dated 31.8.2020. It is clarified that immediate action on the part of RoCs is required as per law, including changing their objects to prevent such companies from carrying out micro-finance activities. Further, the Office of DGCoA shall ensure strict compliance by all the ROCs with the instructions contained in the letters issued earlier by the Ministry on this subject. Further, the ROCs shall also circulate these directions to all the officers/officials to ensure examination in accordance with the law, while processing e-forms relating to Incorporation of Companies and Change in Objects of the MOA of Section 8 companies registered under the Companies Act, 2013.
Other Laws
SEBI
As per Clause 9 of SEBI KYC (Know Your Client) Registration Agency (KRA) Regulations, 2011. The KYC records of all existing clients (who have used Aadhaar as an officially valid document (OVD) shall be validated within a period of 180 days from August 01, 2022. and for those clients who have completed KYC using non-Aadhaar OVD, their records will be validated only after they have given their Aadhaar number.
All Demat accounts maintained by stock brokers should be appropriately tagged. All Demat accounts of stock brokers which are untagged need to be appropriately tagged by June 30, 2022, under the categories which include Proprietary Account to Hold Own Securities; Pool account for Settlement Purposes; Client Unpaid Securities Account to Hold Unpaid Securities of Clients; Client Securities Margin Pledge Account for Margin obligations to be given by way of Pledge/ Re-pledge, and Client Securities under Margin Funding Account to Hold funded securities in respect of margin funding. Further, credit of securities shall not be allowed in any Demat account left untagged from July 01, 2022, onwards. Credits on account of corporate actions shall be permitted. The debit of securities shall also not be allowed in any Demat account left untagged from August 01, 2022. Stock Broker shall obtain permission from Stock Exchanges to allow tagging of such Demat accounts from August 01, 2022, onwards. Stock Exchange shall grant such approval within two working days after imposing the penalty as per their internal policy.
- SEBI has issued a circular to allow Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) to conduct the Annual Meetings of their unitholders and other meetings through video-conferencing and other audio-visual means till the end of December.
Based on the representations received from REITs/InvITs, SEBI has decided to further extend the facility to conduct annual meetings through VC/OAVM. Besides, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), last month, extended the facility of holding AGMs and EGMs through VC/OAVM till December 31, 2022. For conducting such meetings, they need to comply with the procedure prescribed by the regulator. Among other requirements, recorded transcripts of the meetings held through VC or OAVM should be maintained in the safe custody of the investment managers of InvIT or managers of the REIT. Also, InvITs and REITs are required to upload the transcripts on their respective websites as soon as possible after the conclusion of the meetings.
For any dispute between the member and the client relating to or arising out of the transactions in the Stock Exchange, which is of civil nature, the complainant/ member shall first refer the complaint to the IGRC and/ or to Arbitration Mechanism provided by the Stock Exchange before resorting to other remedies available under any other law. A complainant/member, who is not satisfied with the recommendation of the IGRC shall avail the arbitration mechanism of the Stock Exchange for settlement of complaints within three months from the date of IGRC recommendation. For the arbitration application received without going through the IGRC mechanism, the time period of three months will not apply, and for such cases, the limitation period for filing arbitration will be governed by the law of limitation i.e., The Limitation Act, 1963.
The new framework will come into force with effect from 1st June 2022. The Arbitration Mechanism shall be initiated post exhausting all actions for resolution of complaints including those received through the SCORES Portal. The Arbitration reference shall be filed with the Stock Exchange where the initial complaint has been addressed. In case of arbitration matters involving a claim of up to Rs. 25 lakhs, a sole arbitrator shall be appointed and, if the value of the claim is more than Rs. 25 lakhs, a panel of three arbitrators shall be appointed. The arbitration and appellate arbitration shall be conducted at the regional center of the stock exchange nearest to the shareholder(s) /investor(s). The stock exchanges shall preserve the documents related to arbitration for five years from the date of the Arbitral award, appellate arbitral award or Order of the Court, as the case may be; and register the destruction of records relating to the above, permanently. The stock exchanges shall disclose on its website, details of the disposal of arbitration proceedings and details of arbitrator-wise disposal of arbitration proceedings as per the formats prescribed by SEBI for already available arbitration mechanisms.
RBI
The Monetary Policy Committee of the Reserve Bank of India has decided to remain focused on the withdrawal of accommodation to ensure that inflation remains within the target going forward while supporting growth. The Rural cooperative banks can now extend finance to commercial real estate (loans to residential housing projects) within the existing aggregate housing finance limit of 5% of total assets. To further augment customer convenience and facilitate recurring payments like subscriptions, insurance premia and education fees of larger value, the limit per transaction for e-mandate-based recurring payments increased from ₹5,000 to ₹ 15,000.
The directions shall apply to the Non-centrally cleared foreign exchange derivative contracts undertaken in terms of the Foreign Exchange Management (Foreign Exchange Derivative Contracts) Regulations, 2000 and non-centrally cleared interest rate derivative contracts undertaken in terms of the Rupee Interest Rate Derivatives (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2019 and any other non-centrally cleared derivative (NCCD) contract as may be specified by the Reserve Bank. The entities which shall be classified as Domestic Covered Entities under these Directions include Entities regulated by a financial sector regulator (including branches of foreign banks operating in India) and having an Average Aggregate Notional Amount (AANA) of outstanding NCCDs of ₹25,000 crore and above, on a consolidated group-wide basis and Other resident entities having an AANA of outstanding NCCDs of ₹60,000 crore and above, on a consolidated group-wide basis. The Non-resident financial entities have an AANA of outstanding NCCDs of USD 3 billion and above, on a consolidated group-wide basis and Other non-resident entities have an AANA of outstanding NCCDs of USD 8 billion and above, on a consolidated group-wide basis shall be classified as Foreign Covered Entities under these Directions.
FSSAI
Submission of returns physically or through email will not be considered. As per regulation 2.1.13 of Food Safety and Standards (Licensing and Registration of Food Businesses) Regulations, 2011, every licensee shall on or before 31st May of each year, submit a return, in ‘Form D-1’ to the Licensing Authority in respect of each class of food products handled by him during the previous financial year. Provided however that every licensee engaged in manufacturing of milk and/or milk products shall file half yearly returns for the periods 1st April to 30th September and 1st October to 31st March of every financial year in the form D-2, as provided in Schedule-2 of these regulations. Such returns will be filed within a month from the end of the period. A separate return shall be filed for every license issued under the Regulations, irrespective of whether the same Food Business Operator holds more than one license.
View Compliance Calendar
Disclaimer: Information in this note is intended to provide only a general update of the subjects covered. It is not intended to be a substitute for detailed research or the exercise of professional judgment. KNM accepts no responsibility for loss arising from any action taken or not taken by anyone using this publication. Updates are for the period 25.05.2022 till 25.06.2022