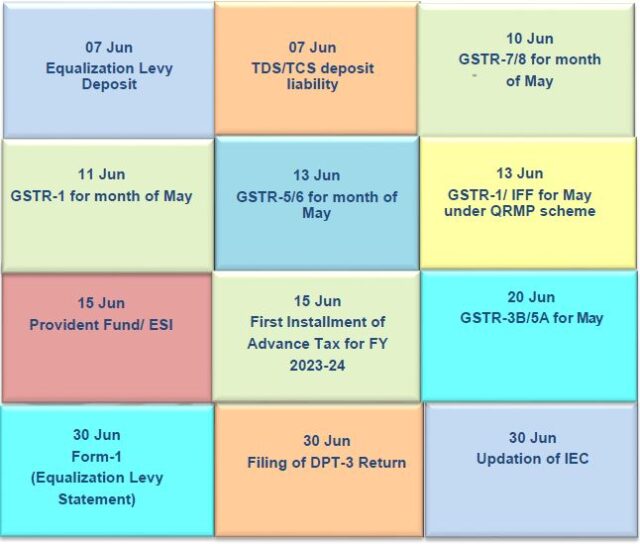
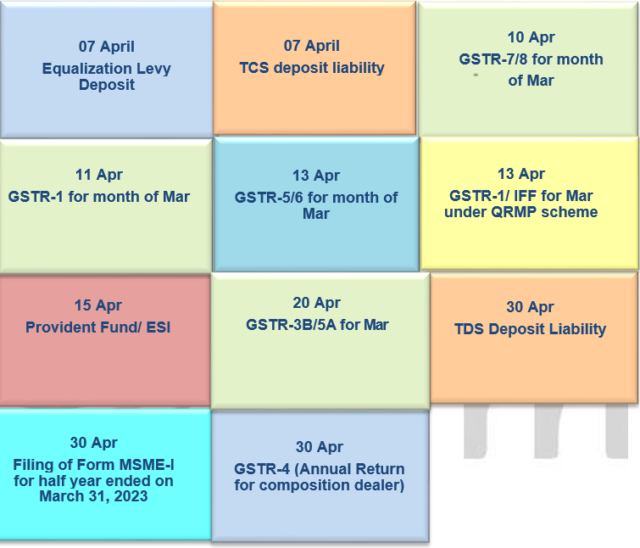
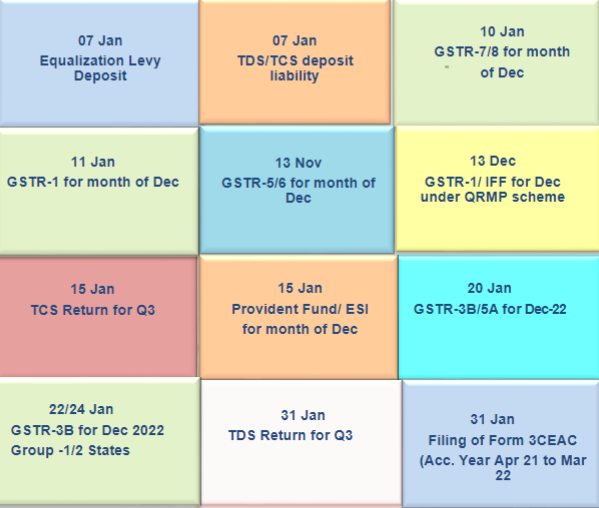
Executive Summary
Income Tax
- New Form 26QF inserted i.e. Quarterly statement of tax deposited in relation to transfer of virtual digital asset u/s 194S to be furnished by an exchange as an alternative to tax deducted by buyer.
- Few exclusions were made from the definition of virtual digital assets.
- New Form 8A inserted for application u/s 158AB to defer filing of appeal before the Appellate Tribunal or the jurisdictional High Court.
- The procedure of PAN application & allotment through Simplified Proforma for incorporating Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) electronically (Form: FiLLiP) of MCA.
Goods & Services Tax (GST) & Customs
- Clarification on various issues relating to applicability of demand and penalty provisions under the CGST Act, 2017 in respect of transactions involving fake invoices.
- Mandatory furnishing of correct and proper information of inter-State supplies and amount of ineligible/blocked Input Tax Credit and reversal thereof in return in FORM GSTR-3B and statement in FORM GSTR-1.
- Exemption from filing annual return of the year to the registered person whose aggregate turnover in the financial year 2021-22 is up to two crore rupees.
Companies Act 2013/ Other Laws.
- Amendment made in Corporate Social Responsibility (“CSR”) Rules.
- NSE has notified a new module for filing of information required under Regulation 46 and 62 of SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015 on NEAPS.
- SEBI has issued a Circular to make an amendment to Investor Grievance Redressal Mechanism regarding the Online Web-Based Complaints Redressal System.
- SEBI has issued a circular to notify that all chargers payable to SEBI shall be subjected to GST at the rate of 18% with effect from July 18, 2022.
- Applicability of GST on services provided by FSSAI.
Income Tax

- CBDT vide Notification No. 73/2022, dated 30/06/2022, inserted a proviso under rule 31A, where the exchange has agreed to pay tax in relation to a transaction of transfer of a virtual digital asset, owned by it as an alternative to the tax required to be deducted by the buyer of such asset u/s 194S, the Exchange shall deliver or cause to be delivered, a quarterly statement of such transactions in Form No. 26QF to the Principal Director General of Income-tax (Systems) or Director General of Income-tax (Systems) or the person authorized by the Principal Director General of Income-tax (Systems) or the Director General of Income-tax (Systems).
“Exchange” means a person that operates an application or platform for transferring virtual digital assets, which matches buy and sell trades and executes the same on their application or platform.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 74/2022, dated 30/06/2022, few exclusions made from the definition of virtual digital asset:
-
- A gift card or vouchers, being a record that may be used to obtain goods or services or a discount on goods or services;
- Mileage points, reward points or loyalty card, being a record given without direct monetary consideration under an award, reward, benefit, loyalty, incentive, rebate or promotional program that may be used or redeemed only to obtain goods or services or a discount on goods or services;
-
Subscription to websites or platforms or applications.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 83/2022, dated 12/07/2022, Form 8A inserted for application u/s 158AB to defer filing of appeal before the Appellate Tribunal or the jurisdictional High Court. Section 158AB provides a procedure where an identical question of law is pending before High Courts or Supreme Court.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 03/2022, dated 16/07/2022 notifies various forms i.e. 3CEF, 10F, 10IA, 3BB, 3BC, 10BC, 10FC, 28A, 27C, 58D, 58C and 68 to be furnished electronically under Income Tax Rules, 1962.
- CBDT vide Notification No. 04/2022, dated 26/07/2022, A Common Application Form (CAF) in the form of Simplified Proforma for incorporating Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) (Form – FiLLiP) has been notified by the MCA. Application for allotment of PAN will be filed in FiLLip form using the Digital Signature of the applicant as specified by the MCA. After the generation of the Limited Liability Partnership Identification Number (LLPIN), MCA will forward the data in form 49A to the Income-tax Authority under its Digital signature.
- CBDT vide circular no. 15, 16, and 17 dated 19/07/2022 condones delay in filing of Forms 9A, 10, 10B, 10BB to extend the powers of Principal Chief Commissioner of Income-tax (Pr. CCIT) / Chief Commissioner of Income-tax (CCIT) where the period of delay is between 365 days to 3 years, for AY 2018-19 and subsequent years.
Goods & Services Tax

- CBIC vide Circular No. 171/03/2022-GST dated 06 July 2022, clarifies various issues relating to the applicability of demand and penalty provisions under the CGST Act, 2017 in respect of transactions involving fake invoices
Issue 1: – In case a registered person (A) issues a tax invoice without a supply of goods and services to another registered person (B), then such an activity does not satisfy the criteria of “Supply” as defined u/s 7 of the CGST Act.
-
- No demand and recovery are required to be made against ‘A’ under the provisions of section 73 or section 74 of the CGST Act.
- No penal action under the provisions of section 73 or section 74 is required to be taken against ‘A’
However, The Registered Person ‘A’ shall be liable for penal action under section 122 (1)(ii) to a penalty of Rs 10,000/- or 10% of the tax due from such person, whichever is higher under the CGST Act for issuing tax invoices without actual supply of goods or services or both.
Issue 2: – In case a registered person (A) issues a tax invoice without a supply of goods and services to another registered person (B). B further issue invoice along with the underlying supply of goods or services or both to his buyers and utilizes ITC availed on the basis of the above-mentioned invoices issued by ‘A’ for payment of outward tax liability.
-
- It is a contravention of the provisions of section 16(2)(b) of the CGST Act, ‘B’ shall be liable for the demand and recovery of the said ITC under the provisions of section 74 of the CGST Act, along with applicable interest under provisions of section 50 of the said Act.
- Also, penal action under the provisions of section 74 is required to be taken against ‘B’.
Further, as per provisions of section 75(13) of CGST Act, if penal action for fraudulent availment or utilization of ITC is taken against ‘B’ under section 74 of CGST Act, no penalty for the same act, i.e. for the said fraudulent availment or utilization of ITC, can be imposed on ‘B’ under any other provisions of CGST Act, including under section 122.
Issue 3: – In case a registered person (A) issues a tax invoice without a supply of goods and services to another registered person (B). B utilizes ITC availed on the basis of the above-mentioned invoice. Further, issue a tax invoice to ‘C’ and passes ITC without the supply of goods or services or both.
-
- There was no supply of goods or services or both by ‘B’ to ‘C’ in respect of the said transaction and also no tax was required to be paid in respect of the said transaction. Therefore, in these specific cases, no demand and recovery of either input tax credit wrongly/ fraudulently availed by ‘B’ in such case or tax liability in respect of the said outward transaction by ‘B’ to ‘C’ is required to be made from ‘B’ under the provisions of section 73 or section 74 of CGST Act.
However, The Registered Person ‘B’ shall be liable for penal action under section 122 (1)(ii) and section 122(1)(vii) to a penalty of Rs 10,000/- or 10% of the tax due from such person, whichever is higher of the CGST Act, for issuing invoices without any actual supply of goods and/or services as also for taking/ utilizing input tax credit without actual receipt of goods and/or services or both.
- CBIC vide Circular No. 170/02/2022-GST dated 06 July 2022, Mandatory furnishing of correct and proper information of inter-State supplies and amount of ineligible/blocked Input Tax Credit and reversal thereof in return in FORM GSTR-3B and statement in FORM GSTR-1.
Furnishing of information regarding inter-State supplies made to unregistered persons, composition taxable persons, and UIN holders – Information sought in Table 3.2 of FORM GSTR-3B is required to be furnished. Along with details on e-commerce operator tax on supplies u/s 9(5) and supplies through e-commerce operator.
Furnishing of information regarding ITC availed, reversal thereof, and ineligible ITC in Table 4 of GSTR-3B –
a) any reversal of ITC or any ITC which is ineligible under any provision of the CGST Act should not be part of Net ITC Available in Table 4(C) and accordingly, should not get credited into the ECL of the registered person.
b) it is clarified that the reversal of ITC of ineligible credit under section 17(5) or any other provisions of the CGST Act and rules thereunder is required to be made under Table 4(B) and not under Table 4(D) of FORM GSTR3B.
c) the registered person is required to identify ineligible ITC as well as the reversal of ITC as per section 16 to arrive at the Net ITC available, which is to be credited to the ECL.
d) Registered person will report reversal of ITC, which are not permanent in nature and can be reclaimed in the future subject to fulfillment of specific conditions, such as on account of rule 37 of CGST Rules (non-payment of consideration to the supplier within 180 days), section 16(2)(b) and section 16(2)(c) of the CGST Act in Table 4 (B) (2).
e) Ineligible ITC on account of the limitation of the time period as delineated in sub-section (4) of section 16 of the CGST Act, which has not been auto-populated in Table 4(A) of GSTR-3B is to be mentioned in others under 4 (D) 2.
- CBIC vide Circular No. 172/04/2022-GST dated 06 July 2022, Clarification on various issue pertaining to GST.
Matter 1: Refund claimed by the recipients of supplies regarded as deemed export
a) The ITC of tax paid on deemed export supplies, allowed to the recipients vide Circular No. 147/03/2021-GST dated 12.03.2021 only for enabling them to claim a refund of such tax paid on the portal, is not ITC in terms of the provisions of Chapter V of the CGST Act, 2017. Therefore, the ITC so availed by the recipient of deemed export supplies would not be subjected to provisions of Section 17 of the CGST Act, 2017.
b) The ITC of tax paid on deemed export supplies, allowed to the recipients for claim refund of such tax paid, is not ITC in terms of the provisions of Chapter V of the CGST Act, 2017. Therefore, such ITC availed by the recipient of deemed export supply for claiming a refund of tax paid on supplies regarded as deemed exports is not to be included in the “Net ITC”.
Matter 2: Clarification on various issues of section 17(5) of the CGST Act.
a) It is clarified that the proviso at the end of section 17(5)(b) of the CGST Act is applicable to the entire clause (b) which is as under:
“Provided that the input tax credit in respect of such goods or services or both shall be available, where it is obligatory for an employer to provide the same to its employees under any law for the time being in force.”
b) It is clarified that “leasing” referred to in section 17(5)(b)(i) refers to the leasing of motor vehicles, vessels, and aircraft only and not to the leasing of any other items. Accordingly, availing of ITC is not barred under section 17(5)(b)(i) of the CGST Act in case of leasing, other than leasing motor vehicles, vessels, and aircraft.
Matter 3: Perquisites provided by the employer to the employees as per contractual agreement.
a) As per Schedule III to the CGST Act provides that “services by an employee to the employer in the course of or in relation to his employment” will not be considered as supply of goods or services and hence GST is not applicable on services rendered by an employee to employer-provided they are in the course of or in relation to employment.
b) Any perquisites provided by the employer to its employees in terms of the contractual agreement entered into between the employer and the employee are in lieu of the services provided by an employee to the employer in relation to his employment. It follows therefrom that perquisites provided by the employer to the employee in terms of the contractual agreement entered into between the employer and the employee, will not be subjected to GST when the same is provided in terms of the contract between the employer and employee.
Matter 4: Utilisation of the amounts available in the electronic credit ledger and the electronic cash ledger for payment of tax and other liabilities.
a) It is clarified that any payment towards output tax, whether self-assessed in the return or payable as a consequence of any proceeding instituted under the provisions of GST Laws, can be made by utilization of the amount available in the electronic credit ledger of a registered person.
b) As per section 49(4), the electronic credit ledger can be used for making payment of output tax only under the CGST Act or the IGST Act. It cannot be used for making payment of any interest, penalty, fees, or any other amount payable under the said acts. Similarly, an electronic credit ledger cannot be used for payment of an erroneous refund sanctioned to the taxpayer, where the such refund was sanctioned in cash.
c) As per section 49(3) of the CGST Act, the amount available in the electronic cash ledger may be used for making any payment towards tax, interest, penalty, fees, or any other amount payable under the provisions of the GST Laws.
- CBIC vide Circular No. 13/2022- Central Tax dated 05 July 2022, Extension of various time limits. This notification shall be deemed to have come into force with effect from the 1st day of March 2020.
Extension of the time limit specified 73(10) for issuance of order u/s 73(9) for recovery of tax not paid or short paid or of input tax credit wrongly availed or utilized, in respect of a tax period for the financial year 2017-18, up to the 30th day of September 2023.
Exclusion of the period from the 1st March 2020 to the 28 of February 2022 for computation of the period of limitation u/s 73(10) of the said Act for issuance of order u/s 73(9) of the said Act, for recovery of erroneous refund.
Exclusion of the period from the 1st March 2020 to the 28th February 2022 for computation of the period of limitation for filing refund application under section 54 or section 55 of the said Act.
- CBIC vide Notification no. 09/2022-Central Tax dated 05 July 2022, notifies and appoints the 5th July 2022, as the date on which the provisions of clause (c) of section 110 and section 111 of the Finance Act 2022 relating to amendment in Section 49 and section 50 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 respectively which relates to Interest on delayed payment of tax on Net liability shall come into force.
- CBIC vide Notification no. 10/2022-Central Tax dated 05 July 2022, hereby exempts the registered person whose aggregate turnover in the financial year 2021-22 is up to two crore rupees, from filing an annual return for the said financial year.
- CBIC vide Circular No. 174/06/2022-GST, dated 06 July 2022, notifies Form GST PMT-03A in case of re-credit in electronic credit ledger equivalent to the amount of erroneous refund sanctioned by the officer and credited to the registered person. Procedure and time limit are defined for the same.
- CBIC vide Notification no. 17/2022-Central Tax dated 01 Aug 2022, the turnover limit for generating e-invoice for B2B supply of goods and services or both or for exports is decreased to exceeding 10 crores from 20 crores. It will be applicable from October 01, 2022.
Companies Act, 2013
- MCA has issued clarification w.r.t. the spending of Corporate Social Responsibility (“CSR”) funds for the “Har Ghar Tiranga” campaign. `Har Ghar Tiranga’, a campaign under the aegis of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, is aimed to invoke the feeling of patriotism in the hearts of the people and promote awareness about the Indian National Flag. In this regard, it is clarified that spending of CSR funds for the activities related to this campaign, such as mass scale production and supply of the National Flag, outreach and amplification efforts, and other related activities, are eligible CSR activities under item no. (ii) of Schedule VII of the Companies Act, 2013 pertaining to the promotion of education relating to culture. Further, the companies may undertake the aforesaid activities, subject to fulfillment of the Companies (CSR Policy) Rules, 2014 and related circulars/ clarifications issued by the Ministry thereof, from time to time.
- MCA has issued a public notice to all the stakeholders that MCA is launching the first set of Company Forms on the MCA21 V3 portal. These forms will be launched on August 31, 2022, at 12:00 AM. Following forms will be rolled out in this phase: DIR3-KYC Web, DIR3-KYC Eform, DPT-3, DPT-4, CHG-1, CHG-4, CHG-6, CHG-8 & CHG-9. To facilitate implementation of these forms in the V3 MCA21 portal, stakeholders are advised to note that the Company e-Filings on the V2 portal will be disabled from 15th Aug 2022 at 12:00 AM for the above 9 forms. All stakeholders are advised to ensure that there are no SRNs in pending payment and Resubmission status. Further, offline payments for the above 9 forms in V2 using the Pay later option would be stopped from August 07, 2022, at 12:00 AM. You are requested to make payments for these forms in V2 through online mode (Credit/Debit Card and Net Banking).
Other Laws
NSE
NSE has notified a new module for filing of information required under Regulation 46 and 62 of SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015 on NEAPS. NSE has directed the listed to furnish information required under Regulations 46 & 62 of Listing Regulations by July 18, 2022. As per Regulation 46 and Regulation 62 of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulation, 2015, the listed entities are required to maintain a functional website containing basic information about the Company. In order to ensure effective enforcement of the Listing Regulations, the Exchange has developed a new module in NEAPS (NSE Electronic Application Processing System) wherein all the listed entities are required to provide the URLs of the information required under Regulations 46 & 62 of Listing Regulations through the prescribed path and for any subsequent modification to be done a separate path is prescribed by the NSE. NSE has further extended the last date of submissions from July 18, 2022, to August 31, 2022, through a separate circular.
SEBI
- The Stock Exchanges have issued a Circular w.r.t maintenance of a functional website containing basic information about the Listed Company under Regulation 46 and Regulation 62 of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) (Listing Obligation and Disclosure Requirements) Regulation, 2015(Listing Regulation). As per the direction by SEBI, all the listed entities are requested to disseminate certain requirements mentioned in sub-regulation 2 of Regulation 46 and sub-regulation 1 of Regulation 62 of Listing Regulation for equity and debt listed entities, respectively, under a separate section on its website. It has been observed that the required disclosures under the aforesaid regulations have been majorly done by the listed entities, but at times, it is cumbersome to locate these disclosures as same are not located in one place along with proper indexing. It has also been observed that the listed entities do not disclose the last amended date of policies uploaded on the website. In view of the above, the listed entities are advised to Disseminate all disclosures, specified under Regulation 46 and Regulation 62 of Listing Regulations, under a separate section as prescribed in the circular. Further, all listed companies have to ensure that their website needs to be updated with the effective date or last amended date of the policies uploaded on the website. All listed entities are therefore advised to take necessary steps to be in compliance with the provisions of this Circular.
- SEBI has issued the consultation paper on the applicability of SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading), Regulations, 2015 to Mutual Fund (MF) units with an objective to extend the applicability of insider trading regulations to units of mutual funds. The intent is to harmonize the regulations governing trading in securities, while in possession of Unpublished Price Sensitive Information (UPSI). In the past, it was observed that a Registrar and Transfer Agent and a few key personnel of a Mutual Fund have redeemed its units or their holdings in the schemes while in possession of certain sensitive information, therefore, to harmonize the provisions in PIT Regulations and to initiate serious enforcement actions against those who misuse the sensitive non-public information pertaining to the scheme of Mutual fund, directly or indirectly, which they have access, by virtue of their fiduciary capacity. Accordingly, PIT Regulations are proposed to be aligned with the SEBI circular by amending the definition of ‘securities’ to do away with the exclusion of MF units; by amending the definition of ‘trading’ to include redeeming, switching, or agreeing to redeem or switch securities; by insertion of Chapter IIA dealing with Restrictions on communication in relation to, and trading by insiders in MF units. Only Chapter IIA. The public comments may be sent via email to pit-mf@sebi.gov.in, no later than July 29, 2022.
- SEBI has notified the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) (Third Amendment) Regulations, 2022 through which it has notified a new chapter X-A which deals with the Social Stock Exchange. The provisions of this Chapter shall apply to a Not-for-profit Organization seeking to get registered with an SSE; To a Not-for-profit Organization seeking to get registered and raise funds through an SSE and to a For-Profit Social Enterprise seeking to be identified as a Social Enterprise under the provisions of this Chapter. The SSE will be accessible only to institutional investors and non-institutional investors. Every SSE will constitute a Social Stock Exchange Governing Council to oversight on its functioning. This chapter also covers the eligibility conditions for being identified as a Social Enterprise. Further, a Not-for-Profit Organization must mandatorily seek registration with an SSE before it raises funds through an SSE. Other features covered under this chapter include Fundraising by the social enterprise; Ineligibility for raising funds; Issuance of Zero Coupon Zero Principal Instruments; Eligibility for issuance of Zero Coupon Zero Principal Instruments; Procedure for public issuance of Zero Coupon Zero Principal Instruments by a Not-for-Profit Organization; Procedure for private issuance of Zero Coupon Zero Principal Instruments by a Not-for-Profit Organization; Contents of the fund-raising document; Deemed compliance with Securities Contracts (Regulation) Rules, 1957; Termination of listing of Zero Coupon Zero Principal Instruments from the Social Stock Exchange.
- SEBI has issued a Circular to make an amendment to Investor Grievance Redressal Mechanism regarding the Online Web-Based Complaints Redressal System. SEBI has implemented an online platform (SCORES) designed to help investors to lodge their complaints, pertaining to the securities market against listed companies and SEBI registered intermediaries. In line with the same, to enable investors to lodge and follow up on their complaints and track the status of redressal of such complaints from anywhere, all Recognized Stock Exchanges including Commodity Derivatives Exchanges/Depositories are advised to design and implement an online web-based complaints redressal system of their own, which will facilitate investors to file complaints and escalate complaints for redressal through Grievance Redressal Committee (GRC), Arbitration, Appellate Arbitration, etc. in accordance with their respective bye-laws, rules, and regulations. SEBI has decided that the Stock Exchanges shall continue with the hybrid mode (i.e., online and offline) of conducting the GRC and Arbitration/Appellate Arbitration process. Further, a client, who has a claim/ counterclaim up to Rs.20 lakh (Rs. Twenty lakh) and files an Arbitration reference, will be exempted from payment of the specified fees. All Recognized Stock Exchanges including Commodity Derivatives Exchanges / Depositories are directed to make necessary amendments to the relevant bye-laws, rules, and regulations for the implementation of the above decision immediately.
- SEBI has issued a circular to notify that all chargers payable to SEBI shall be subjected to GST at the rate of 18% with effect from July 18, 2022. SEBI has instructed that any fees payable by Market Infrastructure Institutions, Companies who have listed/are intending to list their securities, other intermediaries, and persons who are dealing in the securities market, shall be subject to GST. This move has been taken after the GST Council last month recommended withdrawing the exemption granted to services by SEBI and the same was notified on July 13, 2022. The charge would be applicable to all market infrastructure institutions, companies who have listed/are intending to list their securities, other intermediaries, and persons who are dealing in the securities market. Market infrastructure institutions include stock exchanges, clearing corporations, and depositories.
- SEBI has proposed a regulatory framework for the online bond platforms that are selling listed debt securities. Under the proposal, bond platforms should register as stock brokers (debt segment) with the SEBI or be run by SEBI-registered brokers, according to a consultation paper. This will also enhance the confidence among investors, particularly non-institutional investors, as the platforms would be provided by SEBI-regulated intermediaries. Additionally, the stock-broker regulations will be applicable to these entities, which would govern their code of conduct and other aspects related to their operations and risk management. It has been proposed that listed debt securities issued on a private placement basis, and offered for sale on bond platforms should be locked in for a period of six months from the date of allotment of such debt securities by the issuer. The transactions executed on the online bond platforms should be routed through the trading platform of the debt segment of exchanges or through the RFQ (Request for Quote) platform of the stock exchanges, where the transactions will be cleared and settled on a Delivery Versus Payment basis. In addition, the net worth and deposit requirements prescribed for stock brokers will ensure that the bond platform has sound and stable financial health and the applicability of the code of conduct mandated for stock brokers will ensure fairness in their dealings with clients. They will be subjected to regulatory inspection and oversight, providing more confidence to investors and hence, will have the potential to attract more investors. The regulator has sought comments from the public on the proposal till August 12.
- SEBI has notified the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) (Fifth Amendment) Regulations, 2022 through which it has notified a new chapter IX-A which deals with obligations of social enterprises. The provisions of this Chapter shall apply to Profit Social Enterprise whose designated securities are listed on the applicable segment of the Stock Exchange(s) and Not for Profit Organization that is registered on the Social Stock Exchange(s). A Social Enterprise whose designated securities are listed on the Social Stock Exchange(s) or the Stock Exchange(s), as the case may be, shall frame a policy for determination of materiality, duly approved by its board or management, as the case may be, which shall be disclosed on the Social Stock Exchange(s) or the Stock Exchange(s). The board and management of the Social Enterprise shall authorize one or more of its Key Managerial Personnel for the purpose of determining the materiality of an event or information and for the purpose of making disclosures to the Social Stock Exchange(s) or the Stock Exchange(s), as the case may be, under this regulation and the contact details of such personnel shall also be disclosed to the Social Stock Exchange(s) or the Stock Exchange(s). Further, a Social Enterprise, which is either registered with or has raised funds through a Social Stock Exchange or a Stock Exchange, as the case may be, shall be required to submit an annual impact report to the Social Stock Exchange or the Stock Exchange in the format specified by the Board from time to time. The annual impact report shall be audited by a Social Audit Firm employing Social Auditor.
RBI
- RBI has released the Master Direction on Non-Banking Financial Company – Systemically Important Non-Deposit taking Company and Deposit taking Company (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2016. The master direction is revised for the purpose of enabling the Bank to regulate the financial system to the advantage of the country and to prevent the affairs of any Systemically Important Non-Deposit taking Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC-ND-SI) and Deposit taking Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC-D) from being conducted in a manner detrimental to the interest of investors and depositors or in any manner prejudicial to the interest of such NBFCs. Further, this Master Direction has been significantly amended, it has been replaced rather than showing the changes in track mode for reader convenience, and all the changes are listed at the end of Master Direction in any case.
- RBI has issued a notification to relax provisions for overseas investments in the debt market and foreign currency lending by banks, measures which were announced as part of efforts to shore up the rupee. Accordingly, Banks can utilize the funds raised from overseas foreign currency borrowing between July 8 and October 31, 2022, for lending in foreign currency to constituents in India, as per the notification on ‘Overseas foreign currency borrowing of Authorised Dealer Category-I banks. At present, banks can undertake Overseas Foreign Currency Borrowing (OFCB) up to a limit of 100 percent of their unimpaired Tier 1 capital or USD 10 million, whichever is higher. The funds so borrowed cannot be used. Currently, short-term investments by an FPI in government securities (central government securities, including treasury bills and state development loans) and corporate bonds should not exceed 30 percent of the total investment of that FPI in any category. Further, FPIs will be provided with a limited window till October 31, 2022, during which they can invest in corporate money market instruments like commercial paper and non-convertible debentures with an original maturity of up to one year. FPIs can continue to stay invested in these instruments till their maturity or sale. These investments will not be included in reckoning the short-term limit for investments in corporate securities.
- The Reserve Bank of India has released a Circular which allows for International Trade settlements in Indian Rupees (INR). This measure is aimed at facilitating the growth of global trade with emphasis on export from India and to support the interests of the global trading community in Indian rupees. It has also placed an additional arrangement for invoicing, payment, and settlements of exports/imports in Indian rupees. Further, states that the exchange rate between currencies of two trading partner countries may be market determined and the entire process will be carried out using a special VOSTRO account. It is also stated that the Rupee surplus balance accumulated in such account may be used for permissible capital and current account transactions in accordance with mutual agreement. The decision to allow INR in international trade settlements is considered an important step to facilitate trade with Russia, Iran, and Sri Lanka. INR in international trade settlements is also expected to gradually contribute to the global acceptance of rupees for international trade transactions. However, the RBI has given the flexibility that additional surplus generated through exports by partner countries can be invested in Indian government securities and bonds without considering the fact that the rupee is not a convertible currency.
Special Economic Zones
The Ministry of Commerce and Industry has notified the Special Economic Zones (Third Amendment) Rules, 2022 to further amend the Special Economic Zones Rules, 2006. Through this amendment a new Rule 43A which deals with work from home has been notified to provide that a Unit may permit its employees, including contractual employees, to work from home or from any place outside the Special Economic Zone in accordance with this rule. The Unit shall submit its proposal for work from home to the Development Commissioner through email or physical application, which shall contain the terms and conditions of work from home, including the date from which the permission for work from home shall be utilized and the details of the employees to be covered by such permission for work from home. Further, every proposal for permission to work from home or an application for extension of the permit shall be submitted, at least fifteen days in advance, to the Development Commissioner, except in the case of the employees who are temporarily incapacitated or traveling. The proposal for work from home shall cover a maximum of fifty percent of the total employees, including contractual employees, of the Unit and the Unit shall maintain an accurate attendance record for the entire period of permission for work from home and shall submit to the Development Commissioner, from time to time. The Unit may provide to an employee such goods, including a laptop, computer, video projection system, other electronic equipment, and secured connectivity (for virtual private network, virtual desktop infrastructure) to establish a connection between the employee and work related to the project of the unit with the prior permission of the Specified Officer to temporarily remove such goods to the Domestic Tariff Area without payment of duty or integrated goods and services tax.
Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956
The Department of Economic Affairs has issued a notification to declare Zero Coupon Zero Principal instruments as securities under the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956. It is further clarified that “zero coupons zero principal instruments” means an instrument issued by a Not for Profit organization that shall be registered with the Social Stock Exchange segment of a recognized Stock Exchange in accordance with the regulations made by the Securities and Exchange Board of India. The Social Stock Exchange (SSE) is a novel concept in India and such a move is meant to serve private and non-profit sector providers by channeling greater capital to them. Social enterprises eligible to participate in the SSE should be entities — NPOs and for-profit social enterprises having social intent and impact as their primary goal. With regard to fundraising, it has been proposed that eligible NPOs may raise funds through equity, zero coupons zero principal bonds, mutual funds, social impact funds, and development impact bonds. Further, NPOs desirous of raising funds on the SSE will be required to be registered with the exchange. This move will help many organizations including corporates to utilize their fund marked for social responsibility and also help non-profit organizations to get funds in a more transparent manner. In simple words, neither any interest is paid nor principal is repaid under Zero coupon zero principal.
FSSAI
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India has issued clarification regarding the applicability of GST on services provided by FSSAI. It is notified to all stakeholders that GST at the prescribed rate would be applicable on all services provided by FSSAI commencing July 18, 2022. The rates for various services such as the issue of Central license, product approval fee, Food Safety Mitra fee, import clearance fee, etc, will be revised accordingly.
Disclaimer: Information in this note is intended to provide only a general update of the subjects covered. It is not intended to be a substitute for detailed research or the exercise of professional judgment. KNM accepts no responsibility for loss arising from any action taken or not taken by anyone using this publication. Updates are for the period 25.06.2022 till 25.07.2022


![]()
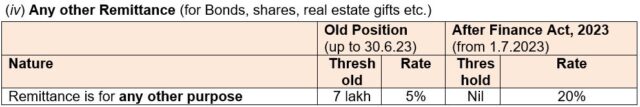
 • CBDT vide Press Release dated 19.05.2023 has clarify that the use of international credit cards for meeting his/her expenses by a person when he is abroad will come under the purview of LRS, earlier only Debit card was covered. Further, to avoid any procedural ambiguity, it has been decided that any payments by an individual using their international Debit or Credit cards upto Rs. 7 lakhs per financial year will be excluded from the LRS limits and hence, will not attract any TCS. Existing beneficial TCS treatment for education and health payments will also continue.
• CBDT vide Press Release dated 19.05.2023 has clarify that the use of international credit cards for meeting his/her expenses by a person when he is abroad will come under the purview of LRS, earlier only Debit card was covered. Further, to avoid any procedural ambiguity, it has been decided that any payments by an individual using their international Debit or Credit cards upto Rs. 7 lakhs per financial year will be excluded from the LRS limits and hence, will not attract any TCS. Existing beneficial TCS treatment for education and health payments will also continue.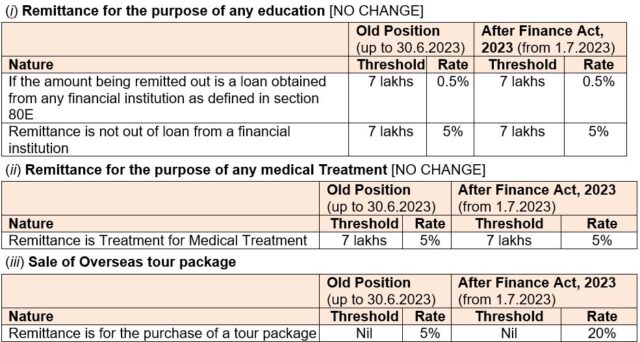
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()